However it’s determined, the discount rate is simply the baseline rate of return that a project must exceed to be worthwhile. NPV accounts for the time value of money and can be used to compare the rates of return of different projects or to compare a projected rate of return with the hurdle rate required to approve an investment. Let’s look at an example of how to calculate the net present value of a series of cash flows. As you can see in the screenshot below, the assumption is that an investment will return $10,000 per year over a period of 10 years, and the discount rate required is 10%. Net after-tax cash flows equals total cash inflow during a period, including salvage value if any, less cash outflows (including taxes) from the project during the period. By using this formula, the investors find out the difference between the cash inflows from the investments and the cost of investments, giving them a clear idea of the profitability of the investment.
NPV Analysis in Excel (XNPV Function)
In order to make sensible investment decisions, you need to look at things from as many different angles as possible. If the result of your calculation is precisely zero, this means that the investment will only make the discount interest. As this means that there is no foreseeable profit, there’s no benefit to this investment. You’d get the same return, possibly at much less risk, if the money sits in a savings account. On the other hand, if your initial investment figure is higher than the total of the present value of future cash, you have a negative net present value.
Create a free account to unlock this Template
For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Profitability is a key indicator of financial health and affects an organization’s ability to reinvest in growth, distribute dividends, or pay down debt. In case of mutually exclusive projects (i.e. competing projects), accept the project with higher NPV.
Evaluating Various Types of Investments
- For example, IRR could be used to compare the anticipated profitability of a three-year project with that of a 10-year project.
- A lower or negative NPV suggests that the expected costs outweigh the earnings, signaling potential financial losses.
- The present value is calculated by discounting future cash flows using a discount rate that reflects the time value of money.
- Once we have the total present value of all project cash flows, we subtract the initial investment on the project from the total present value of inflows to arrive at net present value.
- Put more simply, NPV tells you what the present value of an investment or project (specifically the cash flows) is at a required rate of return (discount rate or hurdle rate).
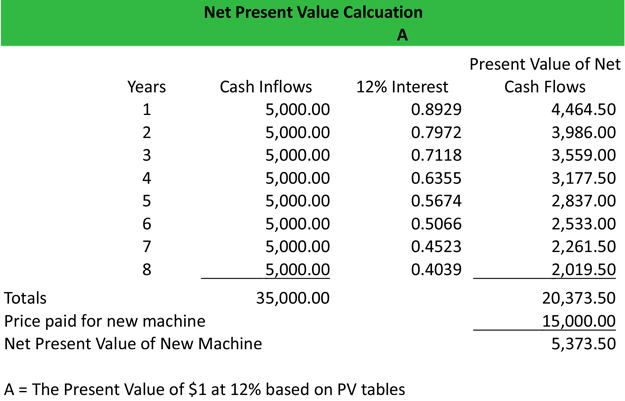
The formula works in the same way, however, each cash flow has to be discounted individually, and then all of them are added together. This can help with decision-making when choosing investments for your portfolio or making strategic capital investments in a business. Net present value calculations can also help companies with projecting future value based on the investments they make today.
You might find it useful if you’re working out whether or not to invest in new equipment for your business. We will start with a very simple example then move onto something a little more detailed. For this first project we are going to assume each year as an even cash flow of $1,000. Most financial analysts production activities never calculate the net present value by hand or with a calculator; instead, they use Excel. Excel’s NPV calculations should be accurate, but they’re only as accurate as the data that’s entered to make the calculation. So, it could be inaccurate, and it’s a good idea to double-check the calculation.
This decision is made to secure a steady income stream with lower risk compared to stocks. The investor assesses the bond’s interest rate, maturity, and the issuing government’s creditworthiness. By investing in bonds, the investor aims to preserve capital while earning interest, balancing their portfolio to mitigate volatility.
This means that you’ll make more in this investment than you would on interest if you put the same amount of money in the bank. As it stands, this leaves an overall return of £50,000 on your £100,000 investment. Now that we know the basics, formula and how to calculate using the net present value method, let us apply the knowledge to practical application through the examples below. Now that we have a basic understanding of the concept and its related factors, let us discuss the formula that shall act as a basis for our understanding of the intricacies of the concept.
If you want to simplify your calculations you could look for an online net present value calculator. Or you could use the NPV function in spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel or something similar. The NPV function helps calculate net present value for an investment based on the discount rate and a series of future cash flows, both positive and negative. One limitation of NPV is that it relies on accurate cash flow projections, which can be difficult to predict.